Multidrug Resistant TB (MDR-TB)
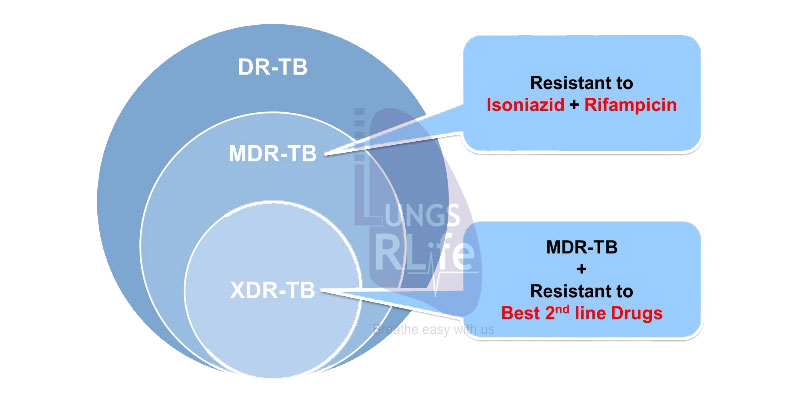
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a type of TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to Isoniazid and Rifampicin which are the First-Line anti-TB drugs. India has the highest MDR-TB rates in the world and Mumbai in particular is the epicentre of MDR-TB epidemic.
MDR-TB can be detected using tests which determine the bacteria for sensitivity to the drugs or detect resistance pattern. These tests can be culture-based or molecular technique.
It is treatable and curable with the use of Second-line drug up to 2 years of treatment. However, Second-line drug options are limited and it requires extensive duration of treatment.
Some of the Second-line drugs are Moxifloxacin, Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Ethionamid, Kanamycin, Cycloserine and Clofazine.
Drug resistance emerges due to mismanagement of the treatment and person-to-person transmission. Mismanagement of treatment can occur through poor quality of drug, poor treatment compliance or incorrect prescription by health care.
This is a dangerous form of TB where the germs have got resistant to the standard drugs. India has the highest MDR-TB rates in the world and Bombay in particular is the epicenter of the MDR-TB epidemic.
This form of TB can only be diagnosed after the culture and sensitivity reports are received from a reliable microbiology laboratory.
It is a difficult form of TB to treat as the drugs needed to cure it have side effects and the duration of treatment is as high as 18 to 24 months. Some of the 2nd line drugs used include: injectable kanamycin, moxifloxacin, PAS, ethionamide, cycloserine, and clofazine.
ADVANCES:
Newer drugs and new diagnostic tests are emerging.